Minutes of 2nd Lecture of Lecture Series on Dimensions of Human Security
Topic of the Lecture: The Economic Dimensions of Human Security: Considerations of the Demand and Supply Policies for War Machinery in Regional Conflicts
Guest Speaker: Dr. Fetus Fatai Adedoyin
Date: April 16, 2021
Time: 01:00 pm
Why Human Security?
When talking about security, we need to realize that security is not always concerned with the military aspect of a conflict, such as war, but it also encapsulates the human aspect which is often overlooked due to an increased emphasis on the traditional modes of security. The complexity of the world keeps bringing new challenges to us, and new forms of threats are always out there. To cope up with such threats, a discourse is required on the concept of Human security. A recent example is the covid 19 pandemic, which came as the most unexpected event of year 2020.
Such unexpected threats can do a lot of damage to the society, and we need to have a coping mechanism to deal with such unexpected threats. A comprehensive approach is required to tackle threats to human security with an integrated manner.
Concept of Human Security:
Human security is a comprehensive approach towards many challenges faced by the humans daily, and the discourse has moved beyond our general understanding of the concept of security. The modern world has problems that were not considered a potential threat to the life of an individual, such as the problem of identity, the freedom of gender associations and many others, that directly concerns an individual. Human security addresses all such threats and it makes it clear that security is a collective approach and many aspects of it overlap on different levels.
Dimensions of Human Security:
- Economic security: problems like unemployment and persistent poverty contribute to the unrest and worry in a society. People need jobs to sustain their livelihood and an absence of employment opportunities makes them available to be used for other purposes.
- Food Security: food is one of the most essential commodities for survival and food insecurity can cause distress among the masses. Poor economic policies and environmental changes can cause famines, food scarcity and widespread hunger which can lead people to be employed in unproductive ways.
- Health security:the significance of a comprehensive global policy for health security was made clear by the Covid 19 pandemic, other than that, health security is required to tackle problems like malnutrition and providing basic health facilities to the people.
- Environmental security: environmental degradationcauses are directly or indirectly linked to the food and economic insecurity within a state which affects farming, fishing and forestation.
- Personal security: security at a personal level is also a fundamental right and it is not exclusive to a person only, but also to his family and loved ones. Everyone has the right to security from theft, abuse, slavery, bonded labor, child labor, imprisonment etc.
- Community security: a recent and a more popular approach towards human security is the dimension of community security, where a community demands security for their collective rights and protection from the existential threats that they face. Communities can be associated with a gender, identity, ethnicity or a race.
- Political security: an unstable political system can produce mass civil unrest among the citizens of a state, and it happens when the people in power are unable to hold up the standards of governance, which results in the gradual destruction of the social fabric of a society.
Economic Dimensions of Human security:
All the dimensions of the human security add back to the economic aspect of human security. Favorable economic conditions can uplift the lives of people and allow them to be put to productive use. Unemployment and persistent poverty create a supply of human resource to be utilized for other purposes that can harm the social fabric of a society. An understanding of the economics of an armed conflict can help better understand the human security problem created due to that conflict.
The economic dimension is influenced by the following agents:
- Consumer behavior
- Firm Motivations
- Government
- International Community
Demand and supply for war machinery:
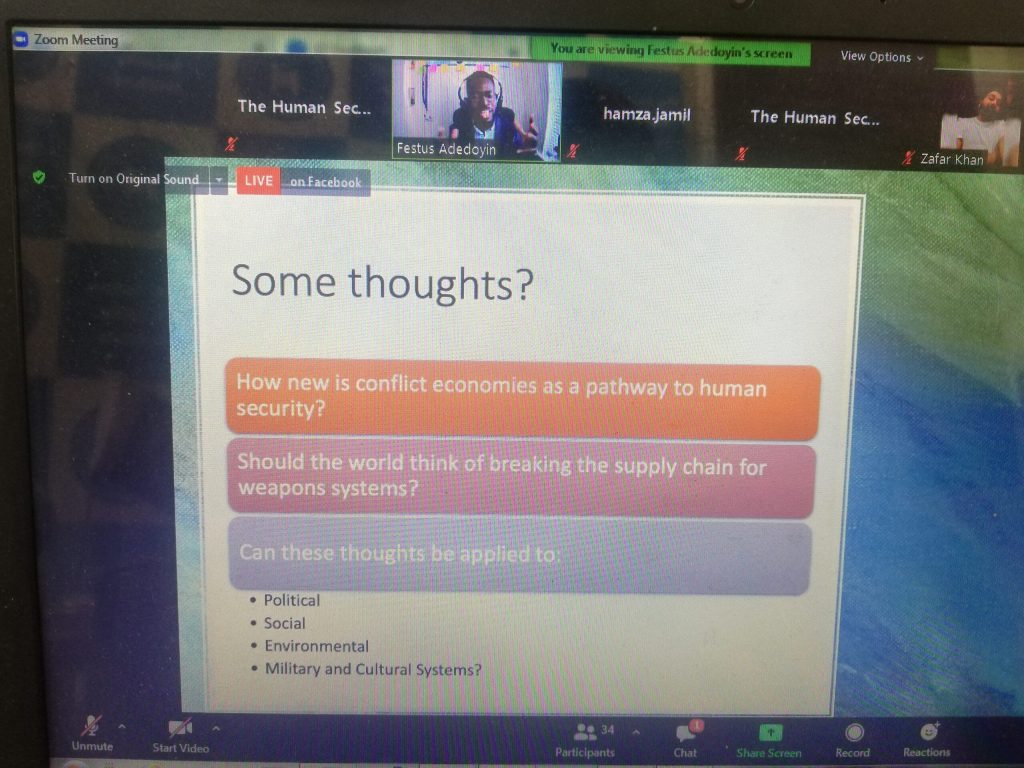
The economics of an armed conflict can be better understood by looking at the demand and supply of arms and weapons in that conflict. An armed conflict comes at a heavy price. Conflicts such as Syrian civil war or the civil war in Yemen damaged the infrastructure, the employment opportunities and businesses of the citizens, but the demand for arms has also risen simultaneously. Middle East is the most heavily armed region in the world despite being the most unstable and prone to armed conflicts. Since the end of the cold war, the arms supply has mostly been between the global north and global south with US being the largest exporter of arms.
A clear demand for arms is there in the region and creates a question that how a region so economically challenged can fund such endeavors. The arms market has grown and there are people profiting from it and certain regions are relentlessly being supplied with arms making them more heavily armed than other regions.
A market for conflict:
Much like market for goods, services and products, there is also a market for conflict. And in a conflict market, a supply creates its own demand. For example, in a country ridden with political instability and poverty, there will be population available to be exploited for other uses which may posse a threat the stability if the region.
Such a situation creates a decline in the working population and increased borrowing by the government, disruption in trade and higher inflation affects the lives of people. The GDP of such a country is locked in a perpetual state of socio-economic instability and the standards of the human development drop significantly. This market is thriving, and it needs to be addressed. Otherwise, the objective of human security can never be achieved.